Rapid Prototyping vs. Low Volume Production: When to Use SLS 3D Printing
Understanding SLS 3D Printing
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a popular 3D printing technology known for its ability to produce strong, functional parts with complex geometries. By using a laser to sinter powdered material, often nylon, SLS can create durable and intricate designs without the need for support structures. This makes it an ideal choice for both rapid prototyping and low volume production.
As industries continue to seek efficient and cost-effective manufacturing solutions, understanding when to employ SLS 3D printing for rapid prototyping versus low volume production is crucial. Both applications have distinct advantages, and knowing which to choose can significantly impact project timelines and budgets.
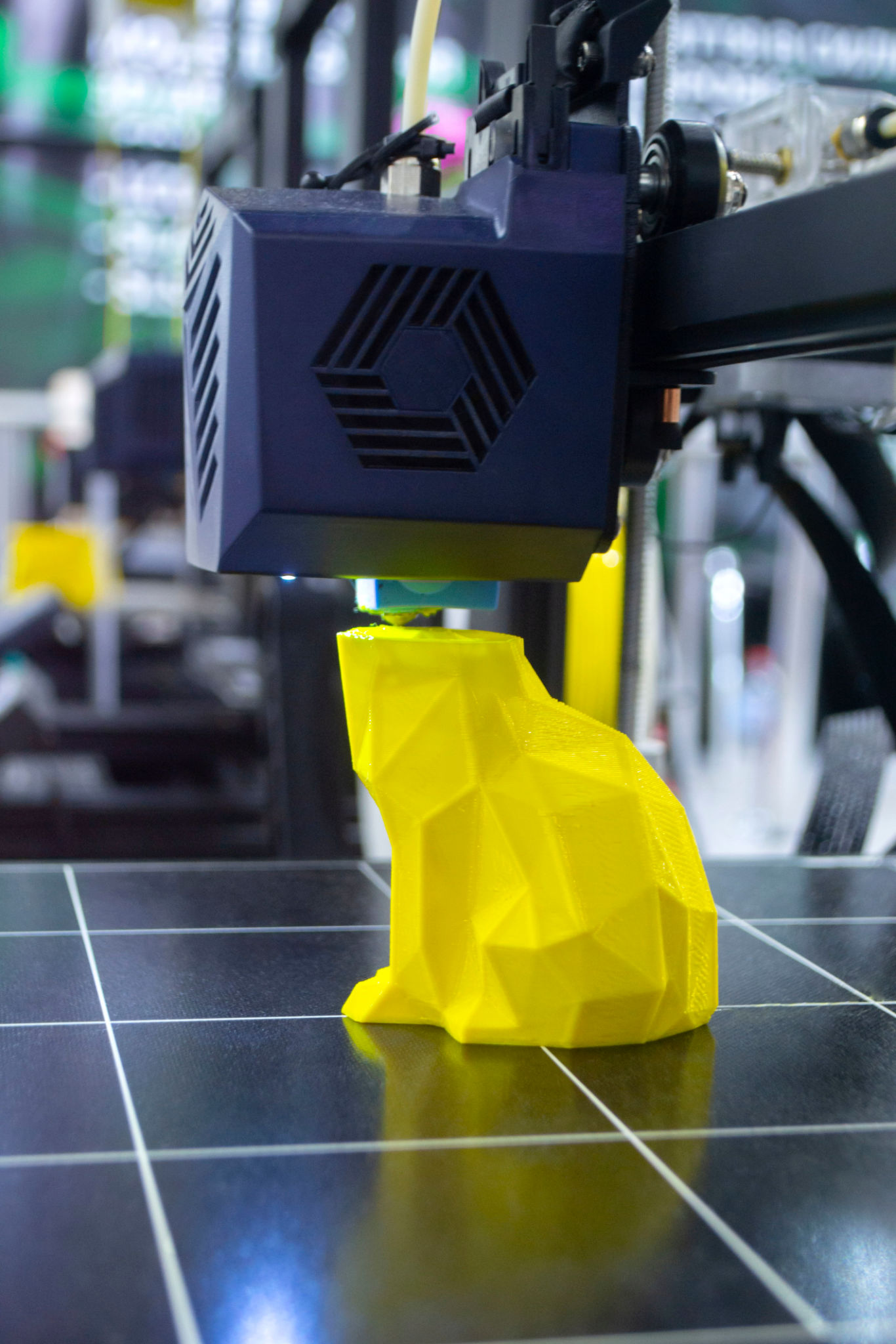
When to Use SLS for Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is an essential stage in product development, allowing designers to test ideas quickly and efficiently. SLS 3D printing is particularly suited for this purpose due to its ability to produce high-resolution prototypes that closely mimic the final product. Here’s when SLS is ideal for rapid prototyping:
- Complex Designs: SLS can handle intricate and detailed designs without the need for support structures, making it perfect for prototypes that need to test complex geometries.
- Functional Testing: The strength and durability of parts made with SLS allow for functional testing, ensuring that prototypes can withstand real-world applications.
- Material Versatility: With a range of materials available, such as nylon, glass-filled nylon, and other composites, SLS can create prototypes that mimic the final product’s characteristics.
By using SLS for rapid prototyping, designers can iterate quickly, reducing the time and cost involved in traditional manufacturing methods.

SLS in Low Volume Production
Low volume production involves the manufacturing of small quantities of a product, usually ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand units. SLS 3D printing offers several advantages in this context:
- Cost-Effectiveness: For small production runs, SLS is often more economical than traditional manufacturing due to the reduced tooling costs and setup times.
- Customization: SLS allows for easy customization and personalization of products, making it ideal for industries like healthcare or consumer goods where bespoke solutions are needed.
- Speed: The ability to produce parts quickly without extensive setup means faster time-to-market for low volume products.
These benefits make SLS an attractive option for businesses looking to produce limited quantities without sacrificing quality or incurring excessive costs.
Choosing Between Rapid Prototyping and Low Volume Production
The decision to use SLS 3D printing for rapid prototyping versus low volume production depends on several factors:
- Project Stage: Determine whether you’re in the initial design phase or ready to produce final products.
- Budget Constraints: Consider the cost implications of each approach based on your available resources.
- Timeframe: Evaluate how quickly you need the parts and choose accordingly.
Understanding these elements will help in selecting the most appropriate use of SLS technology, ensuring optimal results for your project needs.
The Future of SLS 3D Printing
SLS 3D printing continues to evolve, offering even greater flexibility and efficiency. As technology advances, we can expect further improvements in material options, print speeds, and overall capabilities. This evolution will likely expand the applications of SLS in both rapid prototyping and low volume production, providing even more value to industries worldwide.
For businesses looking to stay competitive, embracing SLS technology can lead to innovative solutions that drive success. Whether used for creating prototypes or final products, SLS remains a powerful tool in the modern manufacturing landscape.
