Prototyping with PLA: A Guide for Early Product Development
Understanding PLA and Its Benefits in Prototyping
In the realm of early product development, choosing the right material for prototyping is crucial. Polylactic Acid (PLA) has emerged as a popular choice among designers and engineers due to its ease of use and environmental friendliness. **PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic**, derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugar cane, making it an attractive option for businesses looking to reduce their ecological footprint.
PLA's popularity in prototyping is largely due to its **low melting point**, which allows for smoother printing and less warping. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for those using 3D printers, as it enables more detailed and precise models. Additionally, PLA is available in a wide range of colors, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of prototypes.
The Prototyping Process with PLA
The process of prototyping with PLA often begins with creating a digital model using CAD software. This step allows designers to refine their designs and ensure accuracy before moving on to physical production. Once the digital model is ready, it’s time to 3D print the prototype using PLA filament.
When 3D printing with PLA, it is important to set the printer to the correct temperature—typically between 180°C and 230°C—to ensure optimal results. Additionally, **using a heated bed** can further prevent warping and ensure better adhesion of the material to the printing surface.

Advantages of Using PLA for Early Product Development
One of the standout advantages of using PLA in prototyping is its **cost-effectiveness**. Compared to other materials like ABS, PLA tends to be less expensive, making it a practical choice for startups and small businesses looking to manage their budgets effectively. Furthermore, its biodegradability aligns with the growing trend of sustainable development.
PLA also offers excellent visual quality and surface finish, which are essential for showcasing prototypes to stakeholders or potential investors. Its ability to produce detailed models allows designers to convey their concepts clearly and effectively, facilitating smoother product development cycles.
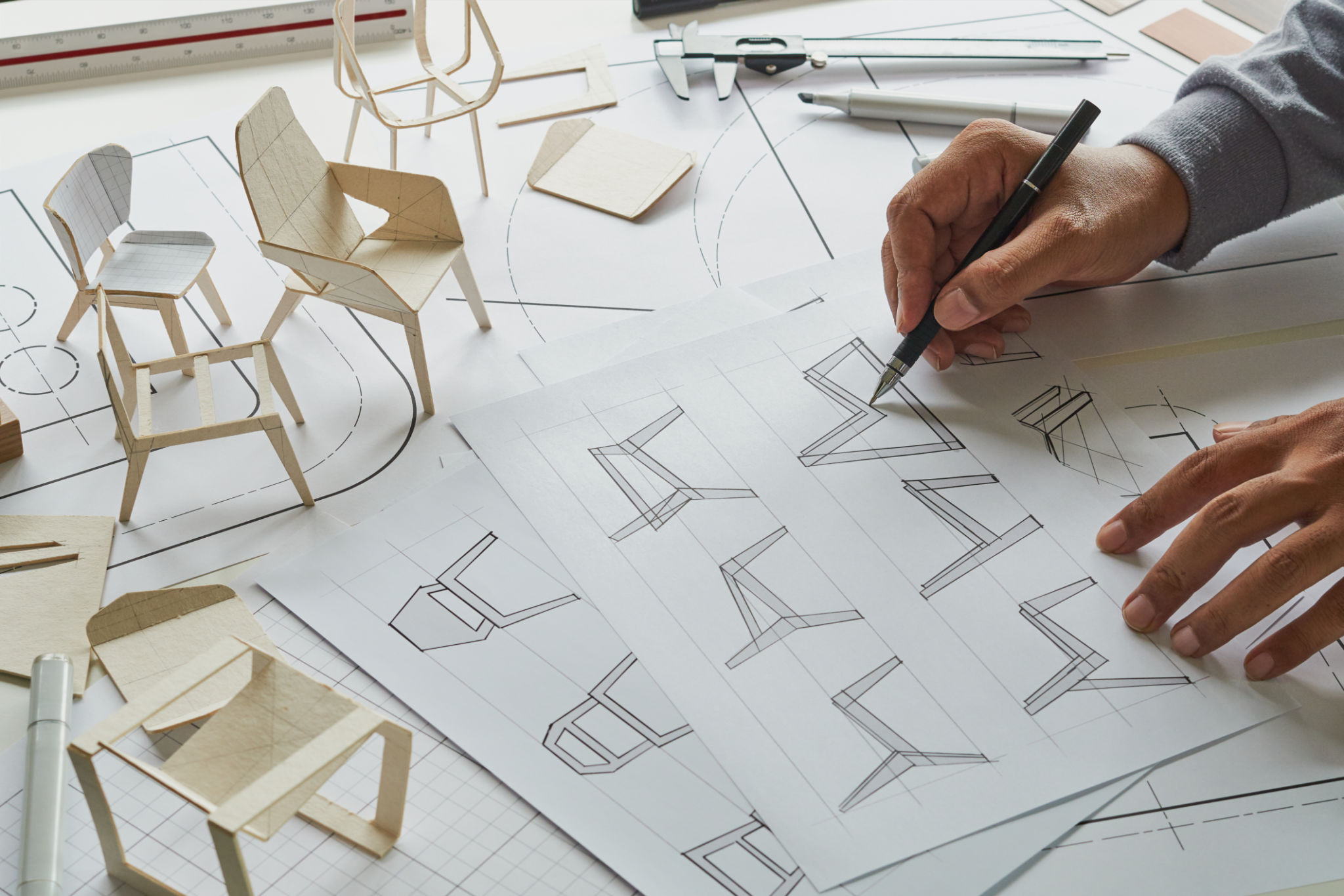

Challenges and Considerations
Despite its many benefits, there are several considerations to keep in mind when using PLA for prototyping. **Strength and durability** may not match that of other materials like ABS or nylon, which can be a limitation for functional prototypes that require more rigorous testing. This means PLA is often better suited for aesthetic prototypes or early-stage models.
An additional challenge is the limited thermal resistance of PLA. Products exposed to high temperatures may deform or lose their shape over time, which is an important factor to consider depending on the intended use of the prototype.
Conclusion: Leveraging PLA in Your Prototyping Journey
In conclusion, PLA offers a compelling blend of benefits for early product development, including cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and environmental sustainability. While it may not be suitable for every application due to its strength limitations, it remains an excellent choice for producing visual models and initial prototypes.
By understanding both the advantages and challenges of PLA, designers and engineers can make informed decisions that align with their project's specific needs. Whether you are a startup or an established business seeking to innovate, **prototyping with PLA** can be a valuable tool in your product development arsenal.